नमस्कार मित्रांनो इयत्ता बारावी Biology या Subject च्या Practical मध्ये PART - B: Demonstration Experiments (Spotting) हा भाग Practical Exam च्या दृष्टीने फार महत्त्वाचा आहे. या Blog Post मध्ये आपण Spotting Practical Number 10: To study the prepared pedigree charts of genetic traits such as rolling of tongue, widow's peak, blood groups and colour blindness ह्या Practical Experiment चे Answer पाहणार आहोत. खाली दिलेल्या उत्तरांमध्ये काही अडचण असल्यास आम्हाला comment करा किंवा तुमच्या संबंधीत विषय शिक्षकांशी चर्चा करा.
B. DEMONSTRATION EXPERIMENTS (Spotting)
10. To study the prepared pedigree charts of genetic traits such as rolling of tongue, widow's peak, blood groups and colour blindness.
Introduction :-
A pedigree is a list of ancestors showing genetic relationships between members of a family.
A record of inheritance of certain genetic traits for two or more generations presented in the form of a family tree or o diagram, is called a pedigree chart. Study of pedigree chart provides a strong tool, which is used to trace the inheritance of a specific trait, abnormality or disease in a family. In pedigree charts specific symbols that are used, are indicated below:
Aim: To Study the prepared pedigree charts of genetic traits such as rolling of tongue, widow's peak, blood groups and colour blindness.
Requirements : Prepared pedigree charts of genetic traits.
Procedure : Observe the given pedigree chart and write comments on it.
1. Inability to roll the tongue :
The rolling of the tongue is the ability of a person to roll the tongue inwards in 'U' shaped as shown in the following figure. The inability to roll the tongue, is caused by autosomal recessive allele 'a'. Both homozygous dominants (AA) and heterozygous (Aa) individuals are able to roll the tongue while homozygous recessive (aa) individuals are unable to roll the tongue.
Pedigree chart for inability to roll the tongue :
Comment on the given pedigree chart with respect to :
1. Inheritance of trait
Rolling of tongue.
2. Number of normal, carriers and affected progeny
Normal: 03, Carrier: 00 (as the trait is dominant), Affected: 06.
3. Linkage - sex linked or autosomal
Autosomal dominant traits.
2. Widow's Peak
Widow's peak is a V-shaped hair line across the forehead. It is a dominant autosomal trait. The gene responsible for the widow's peak is the dominant 'W'. Therefore, both homozygous dominant (WW ) and heterozygous (Ww) individuals have widow's peak, while homozygous recessive (ww) individuals have straight hair lines. This feature is observed with both men and women.
Solution :-
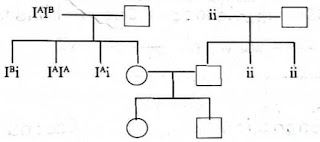
Pedigree chart for blood groups :-
Comment on the given pedigree chart with respect to :
1. Inheritance of trait
Widow's peak
2. Number of normal, carriers and affected progeny
Normal: 03, carrier: 00, Affected: 06
3. Linkage - sex linked or autosomal
Autosomal dominant traits.
3. Human blood groups
1. The blood groups in human beings are described as per ABO system of classification.
2. The gene I (isoagglutinogen) controls the ABO blood groups.
3. It has three alleles; IA, IB, and i (recessive).
4. The alleles IA and IB produce a slightly different form of antigen and allele i (recessive), and do not produce any surface antigen on R.B.Cs.
5. Each individual possesses only two alleles out of three.
6. Alleles IA and IB are co- dominant. Individually they are completely dominant over allele i.
7. There are six different genotypes and four different phenotypes with blood groups which are seen as follows:
| Phenotype | Genotype |
|---|---|
| Blood Group A | IAIA or IAi |
| Blood Group B | IBIB or IBi |
| Blood Group AB | IAIB |
| Blood Group O | ii |
Pedigree chart for blood groups :-
Solution :-
Comment on the given pedigree chart and give the genotypes of the blood groups of individuals marked in blank box numbers - 2, 4, 8, 9, 12, 13 :-
Comment on the given pedigree chart and give the genotypes of the blood groups of individuals marked in blank box numbers - 2, 4, 8, 9, 12, 13 :-
| Box Number | Genotype | Blood Group |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | IAi | A |
| 4 | ii | O |
| 8 | IAIB | AB |
| 9 | ii | O |
| 12 | IAi | A |
| 14 | IBi | B |
4. Colour blindness
1. Colour blindness is a sex / X linked recessive disorder of humans.
2. Due to the recessive gene present on X chromosomes, colour sensitive cone cells are not formed. This results in red-green colour blindness.
3. It is more common in male than females.
4. It follows criss-cross inheritance as this trait is transmitted from the father to the grandson through his carrier daughter.
Pedigree chart for colour blindness :-
Solution :-
Comment on the given pedigree chart with respect to :
1. Inheritance of trait
Criss cross inheritance (Colour blindness)
2. Number of normal, carriers and affected progeny
First generation
1] Normal →00
2] Carrier →03
3] Affected →00
Second Generation
1] 1] Normal →02
2] Carrier →01
3] Affected →01
3. Linkage - sex linked or autosomal
Sex linkage (x-linked recessive disorder).
Questions
1. What is pedigree?
Ans :- A pedigree is a diagram that represents the inheritance pattern of traits or genetic disorders in a family across generations. It helps track the presence or absence of specific traits, illustrating how they are passed on.
2. Why are X-linked disorders more common in males than in females?
Ans :- Males have only one X chromosome, so a single defective gene on it can cause a disorder. Females, having two X chromosomes, are more likely to have a normal copy that compensates for the defective one.
3. What are holandric traits?
Ans :- Holandric traits are those controlled by genes located on the Y chromosome. These traits are passed exclusively from father to son, as only males inherit the Y chromosome.
4. Give an example of an autosomal recessive disorder in humans.
Ans :- Cystic fibrosis is an example of an autosomal recessive disorder. It occurs when an individual inherits two defective copies of the CFTR gene, one from each parent.
5. Explain the concept of co-dominance with respect to the ABO system in humans.
Ans :- In the ABO blood group system, alleles and are co-dominant, meaning both are equally expressed when inherited together. For instance, individuals with genotype have blood group AB, showing characteristics of both A and B antigens.
*PDF Link - Click Me :) or Click on Download Button Below: