1) Aim
2) Apparatus
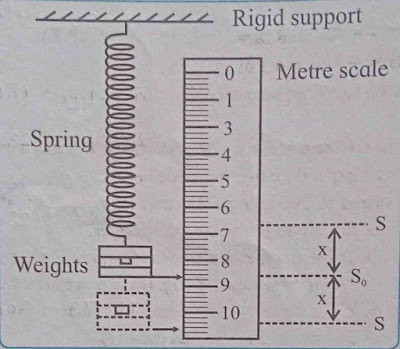
3) Diagram
4) Formula with explanation/law
5) Theory
6) Observations
7) Observation Table
8) Calculation
9) Result/Conclusion
10) Precautions
11) Questions
12) Graph
आता आपण Experiment चे Solutions पाहण्यास सुरुवात करुया :-
Class 12 Physics Practical No 1 : Spring - Mass Oscillator Solutions Maharashtra Board
[Page No 4]
Aim :
a) To determine the force constant (k) of the given spring.
b) To determine the mass of the spring.
Apparatus :
Light spiral with clamping arrangement and attached pointer, meter scale, hanger, weight box, stop watch.
Diagram :
Formula :
1) F = -kx
2) Potential energy (P.E) = 1/2 kx²
3) mass of spring ms = 3 × (x - intercept)
Where, F - is restoring force.
x - is extension of the spring.
k - is force constant of the spring.
Theory :
The period (T) of S.H.M. about the position of equilibrium
T² = 16π²R³N/r⁴n [ M = ms/3 ]
Differentiating above equation, we get
T² = 0,
0 = 16π²R³N/r⁴n [ M = ms/3 ]
M + m/3 =0
M = ms/3
ms = 3 × (x intercept)
ms/3 = x intercept
ms = 3x(x intercept)
Where,
R - Radius of spring
N - No. of turns in the string
r - Radius of the wire used for spring
n - Rigidity of the material of the spring
T - Time period of oscillation
[Page No 5]
Observations :
PART - A To determine force constant (k) and potential energy (P.E.) :
1) Mass of the hanger (m0) = 50 g
2) Mass attached to the hanger = m1 = 250 g, so that spring gets stretched to about triple of its unstretched length. Therefore total mass attached M = (m1 + m0) = 300 g.
3) Position of the pointer when the spring is stretched to about triple of the unstretched length S0 = 24.5 cm.
4) To determine force constant (k) of the spring:
[Page No 6]
| Sr.No. | Mass attached to the spring m gwt |
F=(m-M) gwt |
S cm | Extension S0-S =x cm |
P.E.=1/2 kx2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | -150 | 15.7 | 8.8 | 679 |
| 2 | 150 | -100 | 18.6 | 5.9 | 305 |
| 3 | 200 | -50 | 21.7 | 2.8 | 68 |
| 4 | M=250 | 0 | S0=24.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 300 | +50 | 27.4 | -2.9 | -73 |
| 6 | 350 | +100 | 30.2 | -5.7 | -284 |
| 7 | 400 | +150 | 33.1 | -8.6 | -648 |
Observations :
PART - B To determine the mass of spring (ms) :
1) Mass of the hanger (m0) = 50 g
2) Least count of the stop watch = 1 s
| Sr.No. | Total Mass M kg |
Time t for 20 oscillation (s) |
mean t (s) |
Periodic time T=mean t/20 (s) |
T2 (S2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||
| 1 | 350 g | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 0.95 | 0.9025 |
| 2 | 300 g | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 0.85 | 0.7225 |
| 3 | 250 g | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 0.8 | 0.64 |
| 4 | 200 g | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 0.7 | 0.49 |
| 5 | 150 g | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 0.65 | 0.4225 |
Calculation :
1) force constant k of the spring = slope of graph of F against extension X
= 17.54 gwt/cm.
= 17200.864 dyne/cm.
2) potential energy = 1/2 kx²
1/2 k = 1/2 × (17.54) = 8.77
i) 1/2 kx² = 8.77 × 8.8² = 679
ii) 1/2 kx² = 8.77 × 5.9² = 305
iii) 1/2 kx² = 8.77 × 2.8² = 68
iv) 1/2 kx² = 8.77 × (-2.9)² = -73.7557
v) 1/2 kx² = 8.77 × (-5.7)² = -284.9373
vi) 1/2 kx² = 8.77 × (-8.6)² = -648.6292
[Page No 7]
Result :
1) Force constant of the given spring (k) = 17200.8641 dyne/cm
2) Mass of the given spring (ms) from the graph of T² against M = 150 g
3) The graph shows that potential energy of oscillator changes with distance x from equilibrium. The nature of graph is parabolic.
Precautions :
1) Record the mean position of the pointer carefully.
2) Oscillation of the spring mass oscillator should be in a vertical plane.
3) The pointer should move freely over the scale such that it should not touch the scale.
4) Spiral spring should not be stretched beyond the elastic limit.
[Page No 8]
Questions :
1) What are damped oscillations?
Ans : Damped oscillations refer to repetitive movements that gradually decrease in amplitude over time due to the dissipation of energy.
2) Define linear S.H.M.?
Ans : Linear Simple Harmonic Motion (S.H.M.) is a periodic back-and-forth motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement from the equilibrium position.
3) What are forced oscillations?
Ans : Forced oscillations refer to the periodic motions of a system caused by an external periodic force or driving force.
4) Define force constant
Ans : Force constant is a measure of the stiffness or rigidity of a spring or elastic material, representing the force required to extend or compress it by a certain amount.
Graphs :
1) Graph of F against x
2) Graph of P.E. against x
3) Graph of T² against m
तुम्हाला या solutions ची PDF Download करण्यासाठीं पुढील लिंक वर क्लिक करा :-
पुढील Experiment/Practical चे Solutions पाहण्यासाठी "NEXT" button वर क्लिक करा. मागील Experiment/Practical चे Solutions पाहण्यासाठी "Previous" button वर क्लिक करा.
« Previous
Next »