नमस्कार मित्रांनो इयत्ता अकरावी Biology या Subject च्या Practical मध्ये PART - A: Experiments to be performed हा भाग Practical Exam च्या दृष्टीने फार महत्त्वाचा आहे. या Blog Post मध्ये आपण Practical Number 1: Study the parts of microscopes ह्या Practical Experiment चे Answer पाहणार आहोत. खाली दिलेल्या उत्तरांमध्ये काही अडचण असल्यास आम्हाला comment करा किंवा तुमच्या संबंधीत विषय शिक्षकांशी चर्चा करा.
A. EXPERIMENTS TO BE PERFORMED
1. Study the parts of microscopes.
Aim :- To study the parts of a compound microscope and their functions.
Requirements :- Compound Microscope, Simple Microscope
Principle :- A compound microscope is an indispensable instrument in any biological laboratory. It is used for passive observation of structural details of a cell, tissue or organ in sections. A monocular compound microscope and simple microscope are normally used in the biology laboratory. A modern compound microscope has the following structural components as non-optical and optical.
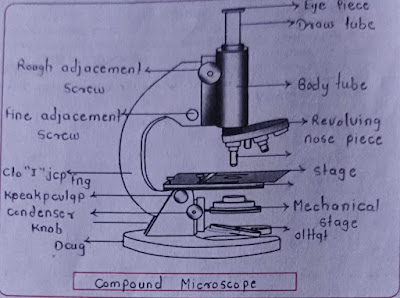
Non-Optical Components :-
1. Base (Foot): It is U or horseshoe-shaped metallic structure that supports the whole microscope.
2. Arm (Limb): It is a curved metallic handle that connects with the base by inclination joint. It supports the stage and body tube.
3. Inclination Joint: It is used for tilting the microscope if required for observation in a sitting position.
4. Stage: It is a metallic platform with a central hole fitted to the lower part of the arm. Microscopic slides are held on the stage by either simple side clips or by a mechanical stage clip.
5. Body tube: It holds ocular and objective lenses at its two ends. The end holding ocular lens is called the head while the end containing 3-4 objective lenses is called a nose piece. The body tube has an internal pathway for the passage of light rays which form the enlarged image of microscopic objects.
6. Draw tube: It is a small tube that remains fixed at the upper end of the body tube. It holds an eyepiece or ocular lens.
7. Adjustment screws: There are two pairs of screws for moving the body tube in relation to stage, larger for coarse adjustment and smaller for fine adjustment.
a. In coars adjustment, the body tube moves up/down.
b. In fine adjustment, the body tube moves up/down, but in extremely short distances.
The coarse adjustment is meant for movement of the objective lens to a proper distance from the object so as to form an image of the same at the ocular end. Fine adjustment is required to obtain a sharp image.
Optical Components :-
1. Ocular Lens or Eyepiece: It is the lens through which the image of the microscopic object is observed. It also takes part in magnification. Depending upon magnification and as per requirements the eye piece can be used normally 5x to 20x.
2. Objective Lenses: They are fitted under the nose piece. Objective lenses are of three types -i) low power (commonly 10X or 5X), ii) high power (commonly 45X) iii) oil immersion (commonly 100X, or more). An objective lens is not a single lens but a compound lens. It forms a real inverted image of the object inside the body tube.
3. Diaphragm: It is flitted just below the stage for regulating the amount of light reached on the object. Diaphragm is of two types, disc and iris.
4. Condenser: It is attached below the diaphragm. The condenser can be moved up and down.
5. Mirror: It is attached just above the base. Both its surface bear mirrors, plane on one side and concave on the other side. Plane mirror is used in strong natural light and a concave mirror in weak artificial light. Mirror directs the light on the object through the condenser and diaphragm system.
Types of Microscopes :- Various types of microscopes are available. The microscopes have varied applications and modifications that contribute to their usefulness.
1. Simple microscope
2. Dissecting microscope
3. The fluorescent microscope
4. Electron microscope
5. Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
6. The scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Microscope, as the name indicates, is an instrument designed to magnify objects which are not visible to the human eye. The microscope was invented by Anton von Leeuwenhoek in 1675 A. D.
A dissecting microscope is a simple microscope with a single lens. It is used to dissect the small organisms or their parts. Dissection of housefly, Cockroach, Drosophila, parts of flower etc. are generally studied under dissecting microscopes. The organism to be studied is kept on the stage and the lens is adjusted with the help of an adjustment screw to get a sharp image. In this microscope lenses of 5X, 10X or 45X are used.
A compound microscope has much higher resolving power than a simple microscope. Under these small organisms, tissues and cells can be easily studied.
Generally the microscopes which we use in biology laboratories are dissecting and compound microscopes with monocular settings. Research and pathology laboratories use binoculars and electron microscopes.
Magnification through a microscope :- To get the total magnification take the power of the objective (5X, 10X, 45x) and multiply by the power of the eyepiece, usually 10X.
Resolution of microscope :- The resolution of an optical microscope is defined as the smallest distance between two points on a specimen that can still be distinguished as two separate entities.
Resolution is the power of an optical instrument to capture and produce more details of an image while magnification is the power of an instrument to create and produce a much larger image of an object. Although both are dependent upon each other, a high magnification does not always guarantee a high resolution.
Directions for use of Microscope :-
1. Clean the stage and with soft cloth or filter paper.
2. Set low power objective in its correct position first.
3. Keep the condenser up and the diaphragm in open position. Focus light with the help of concave mirror. Avoid direct light form the sun and intense light bulb.
4. Clean the lower surface of the slide before placing it on the stage.
5. View through eyepiece and rotate coarse adjustment knob till you see the image of object.
6. Adjust condenser and diaphragm for better resolution.
7. For the clear image, rotate fine adjustment knob.
8. Adjust slide to view desired portion.
9. Clean the microscope before you leave the place.
Precautions :-
1. Always pick up a microscope using both hands, one hand holding the arm of the microscope and the other supporting its base.
2. Although it may seem tempting, never grab or carry a microscope by its eyepiece.
3. When you put the microscope down again, be sure to do so on a flat surface, such as a tabletop.
4. Mirror of the microscope must be facing a light source.
5. Lenses should be cleaned before and after using a microscope.
Activity :
1. Explain the difference between two instruments and give labels to the diagrams.

Questions
1. Complete the following table.
Ans :-
2. Complete the blank spaces of the following paragraph by using information, which you studied regarding the compound microscope. (low power lens, parfocal, ocular lens, light, greatest, low power, higher power, closes)
Ans :- The eyepiece, also called the ocular lens is a low power lens objective lenses of compound microscopes are parafocal You do not need to refocus (except for fine adjustment) when switching to a higher power if the object is in focus on a lower power. The field of view is widest on the lowest power objective. When you switch to a higher power the field of view is closes in. You will see more of an object on low power. The depth of focus is greatest on the lowest power objective. Each time you switch to a higher power, the depth of focus is reduced. Therefore a smaller part of the specimen is in focus at higher power. The amount of light transmitted to your eye is greater at the low power When you switch to a higher power, light (and therefore resolving power, or the ability to distinguish two nearby objects as separate) is reduced. Compensate with the light control (sometimes called the iris diaphragm).
3. How will the wavelength of light affect the magnification of a microscope.
Ans :- The range of visible light wavelengths spans from 380 nm to 750 nm. The wavelength of light affects the resolution and magnification of a microscope. The relationship between wavelength and resolution is inverse: as the wavelength increases, the resolution decreases, which can affect the clarity and detail observed through the microscope. However, magnification itself is not directly impacted by wavelength; rather, the quality of the image and the level of detail visible are influenced.
4. Which are the part of compound microscope that controls the intensity of light entering the viewing area? How?
Ans :- The part of a compound microscope that controls the intensity of light entering the viewing area is the diaphragm, which is located below the stage. The diaphragm adjusts the amount of light reaching the specimen by varying the size of the aperture through which light passes. Many high-quality microscopes are equipped with an Abbe condenser, which includes a built-in diaphragm for precise control of light intensity.
5. Which precautions you have taken in porating of microscope?
Ans :- 1. Always carry the microscope by grasping the arm with one hand and supporting the base with the other hand to ensure stability.
2. Never lift or carry the microscope by its eyepiece, even though it might be tempting. Always place the microscope on a flat, stable surface like a tabletop when not in use.
3. Although microscopes may seem sturdy, they are actually fragile, particularly the glass lenses and delicate focusing mechanisms. Handle them with care to avoid damage.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is not component of compound microscope
a. Stage
b. Base
c. Electron gun
d. Eyepiece
Ans :- c. Electron gun
2. ... collect the light passing through object
a. Objective lens
b. Condenser lens
c. Eyepiece
d. Mirror
Ans :- b. Condenser lens
3. Which of the following regulates the amount of light passing through the slide specimen on the microscope stage?
a. Diaphragm
b. Eyepiece
c. Objective lens
d. Body tube
Ans :- a. Diaphragm
4. A student wants to view cells under the compound microscope at a total magnification of 400X. If the eyepiece is 10X, which of the following objective lenses should be used?
a. 10X
b. 15X
c. 40X
d. 20X
Ans :- c. 40X
5. Movement of slide on stage towards right side, make the image go ..... Side.
a. Right
b. Top
c. Left
d. Bottom
Ans :- c. Left
6. Which of the following light is suitable for maximum resolution.
a. Red
b. Blue
c. Green
d. Orange
Ans :- b. Blue
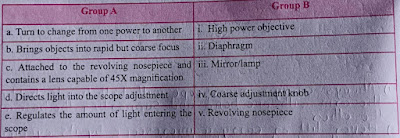
7. Match the microscope parts listed with the correct function.
Ans :-
b) - iv
c) - i
d) - iii
e) - ii
*PDF Link - Click Me :) or Click on Download Button Below: